AI-Ready Next-Gen Memory Circuits (Neuromophic ReRAM CBA)
During my research TA at Korea University, the research team built and integrated a simulation-accurate RRAM cross-bar (CBA) circuit stack for AI workloads: compact parasitics, Verilog-A behavior models, array partitioning, and off-chip learning hooks for SLP/MLP experiments.
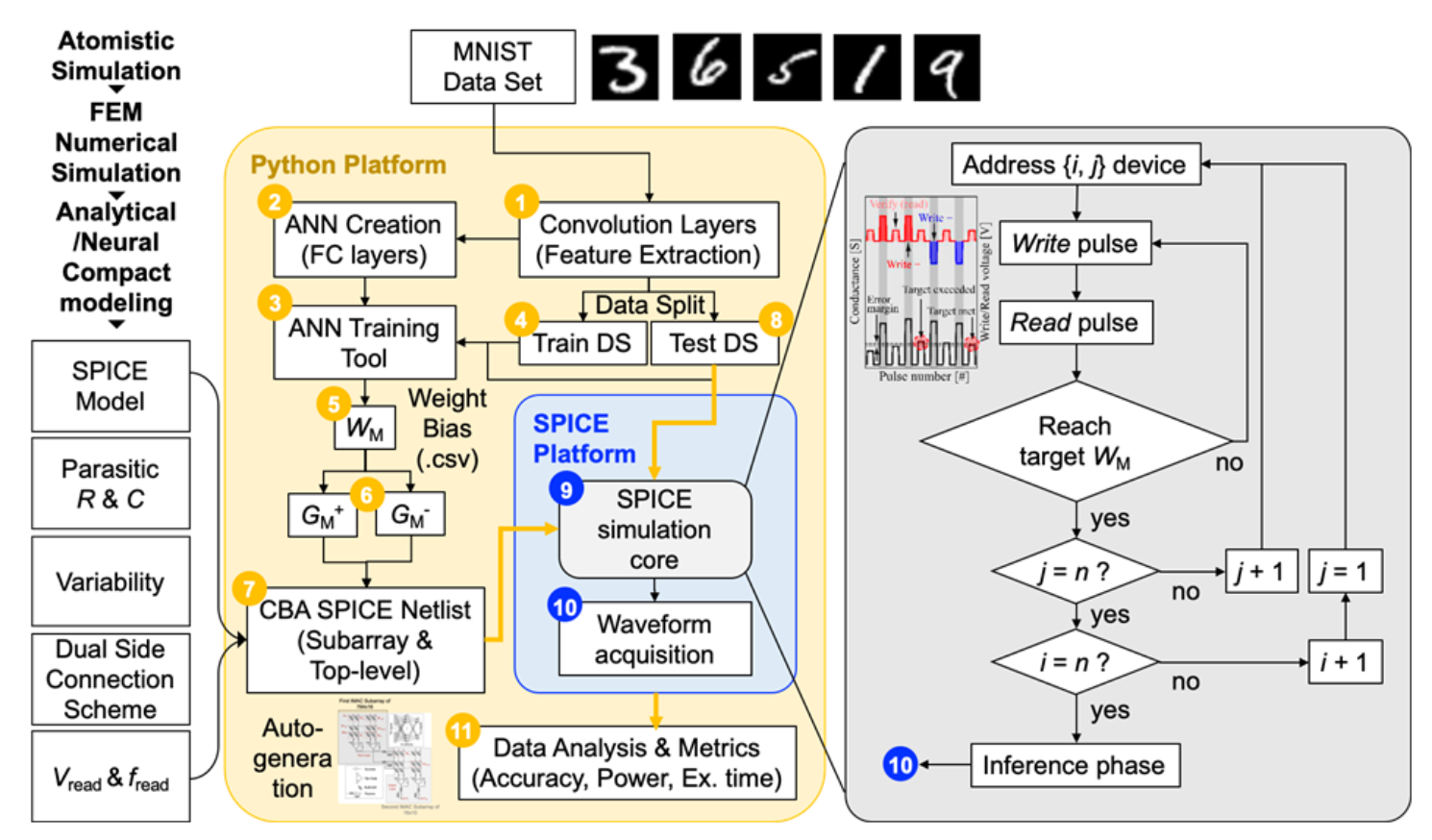
LeNet-5 for MNIST and a heterogeneous CPU–IMAC in-memory analog computing architecture.
-
Scope
Scalable 4×4 1T1R to 120x84x10 Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) arrays, WL/BL/SL routing, and IMAC-style subarray generation. Included resistive/capacitive parasitics and measured their impact on I–V / I–t / V–t behavior.
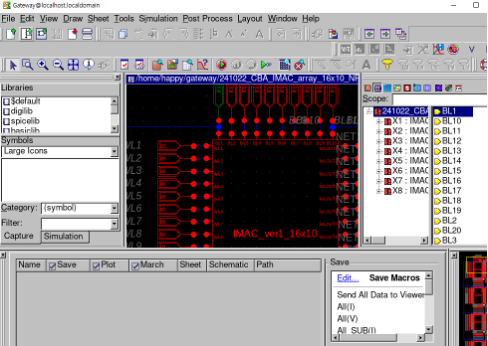
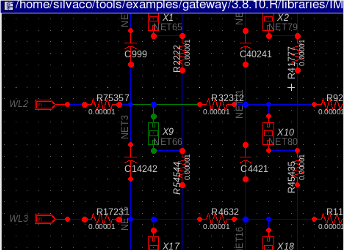
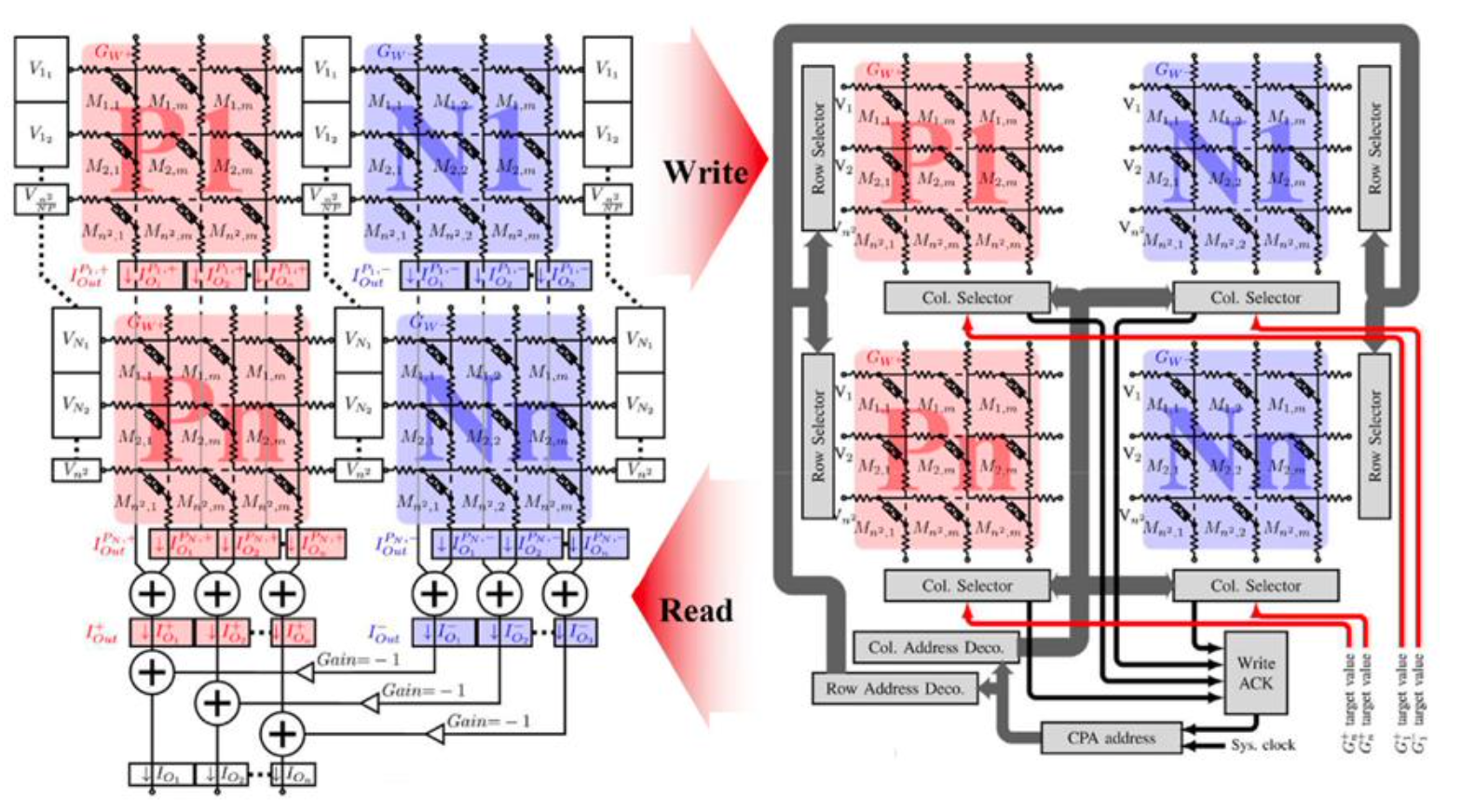
-
Method (Brief)
Build compact CBA + neuron blocks → integrate Verilog-A device/clock models → include line parasitics → connect off-chip training (weights → conductance) → run SPICE batches and analyze accuracy/latency trade-offs.
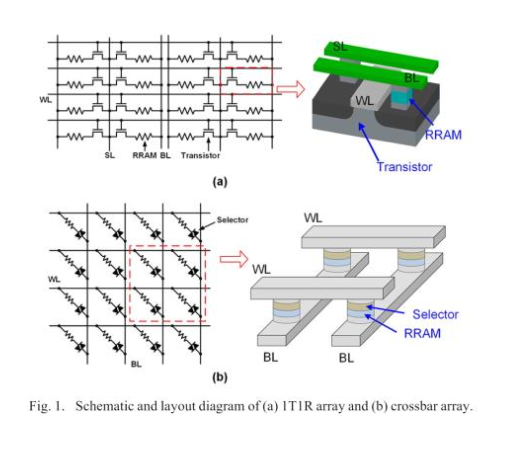
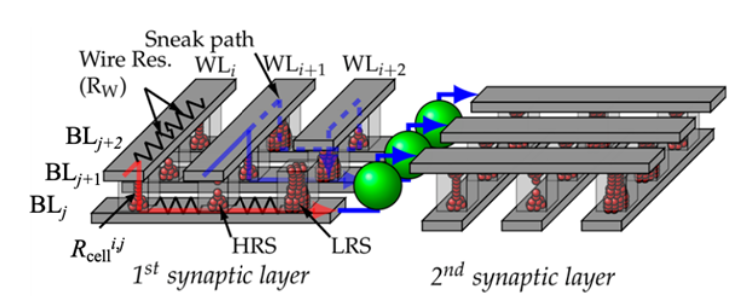
-
System & Integration
• Parasitic modeling: word/bit-line R/C extraction → compact inclusion in netlist.
• Array scaling: verified 4×4 1T1R; profiled 64×64 with/without parasitics; optimized netlisting flow for runtime.
• Learning loop: off-chip SLP/MLP → weight mapping → target conductance; IMAC subarray builder for connectivity.
• Driver blocks: Verilog-A clock/pulse for write-verify; stop-on-target conductance; duty-cycle sweep utility. -
Outcome & Discussion
• Accuracy vs. Parasitics: Captured series-resistance and cap-loading effects across I–V and time-domain curves, informing routing/partition plans.
• Programming Dynamics: Within the safe Vwrite region, write time is far more sensitive to pulse amplitude and duty than frequency, matching DMM-based guidance; frequency-induced threshold shifts still bound the valid window.
• Neuromorphic Relevance: The flow aligns with memristor models showing gradual LTP/LTD and volatile behaviors (IGZO/SnOx) that enable low-power learning and even reservoir computing.
• Scaling Readiness: Embedded Verilog-A plus partitioned arrays gave stable convergence and tractable runtime for large CBAs. -
Tech Stack
SmartSpice, Gateway, Verilog-A, MATLAB/Python (weight mapping), custom netlist generators.
References
• Aguirre et al., “SPICE Simulation of RRAM-Based Cross-Point Arrays Using the Dynamic Memdiode Model,” Frontiers in Physics (2021).
• Lee et al., “IGZO/SnOx-based dynamic memristor with fading memory effect for reservoir computing,” J. Chem. Phys. (2023).